Introduction
In the vibrant investment landscape of Southeast Asia, Vietnam continues to stand out as a prime destination, attracting investors eager to leverage the region’s dynamic growth. In 2024, Vietnam’s digital economy is projected to surpass $45 billion by 2025 (e-Conomy SEA,2023), driven by strong economic fundamentals and an ongoing shift towards high-tech industries and digital transformation. Yet, alongside these promising opportunities, investors must navigate a range of challenges, from regulatory complexities to evolving market dynamics. In this report, we explore Vietnam’s Investment Landscape for 2024, examining the expectations that fuel investor interest and the obstacles and opportunities that define this thriving environment. This landscape delves into the factors shaping Vietnam’s role as a key player in Southeast Asia’s economic future.
Vietnam Investment Landscape 2024 Overview
The Vietnam Investment Landscape 2024 reflects a dynamic and resilient economy, poised for substantial growth across several sectors. Vietnam’s GDP is forecasted to grow around 6% this year, driven by robust manufacturing and strong domestic consumption. While moderated by global uncertainties, this growth trajectory remains one of the most promising in the region. Inflation is largely under control, owing to proactive fiscal measures, although fluctuations in international commodity prices may introduce some variability.( Vietnam 2024 Outlook | The Investor’s Guide to Growth – KPMG Vietnam )
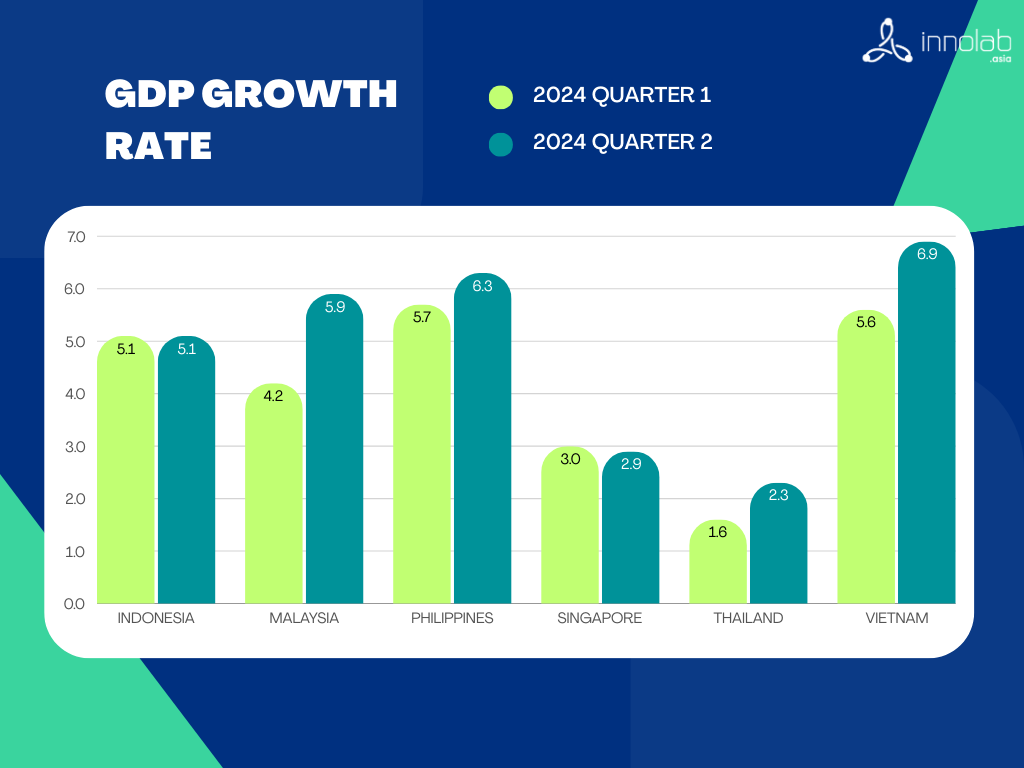
Source : Countries’ national statistics offices ; Oxford Economies
Vietnam’s investment landscape in 2024 is marked by significant foreign direct investment inflows, particularly in high-tech industries. The country attracted over $18 billion in FDI during the first seven months of the year, a 10.9% increase compared to last year. This growth highlights Vietnam’s appeal as a hub for manufacturing and high-tech industries, supported by government incentives and a skilled labor force. These developments position Vietnam as a competitive destination in the global investment arena (Acclime, Vietnam Investment Snapshot (2024)).
Future Plans and Activities in Vietnam
Vietnam has ambitious investment plans for 2025, focusing on several key areas to enhance its economic growth and global competitiveness. These plans include significant investments in infrastructure, green growth, and digital transformation.
Digital Transformation and High-Tech Sectors:
Vietnam’s government continues to place significant emphasis on accelerating digital transformation, particularly in sectors like energy, telecommunications, and banking. This is part of a broader strategy to enhance competitiveness and make Vietnam a hub for tech development within Southeast Asia. The digital transformation is expected to drive growth in e-commerce, fintech, and smart city projects, with AI and IoT as key enablers. This initiative aims to digitize administrative procedures and to transition 90% of them to online platforms through the public services portal.
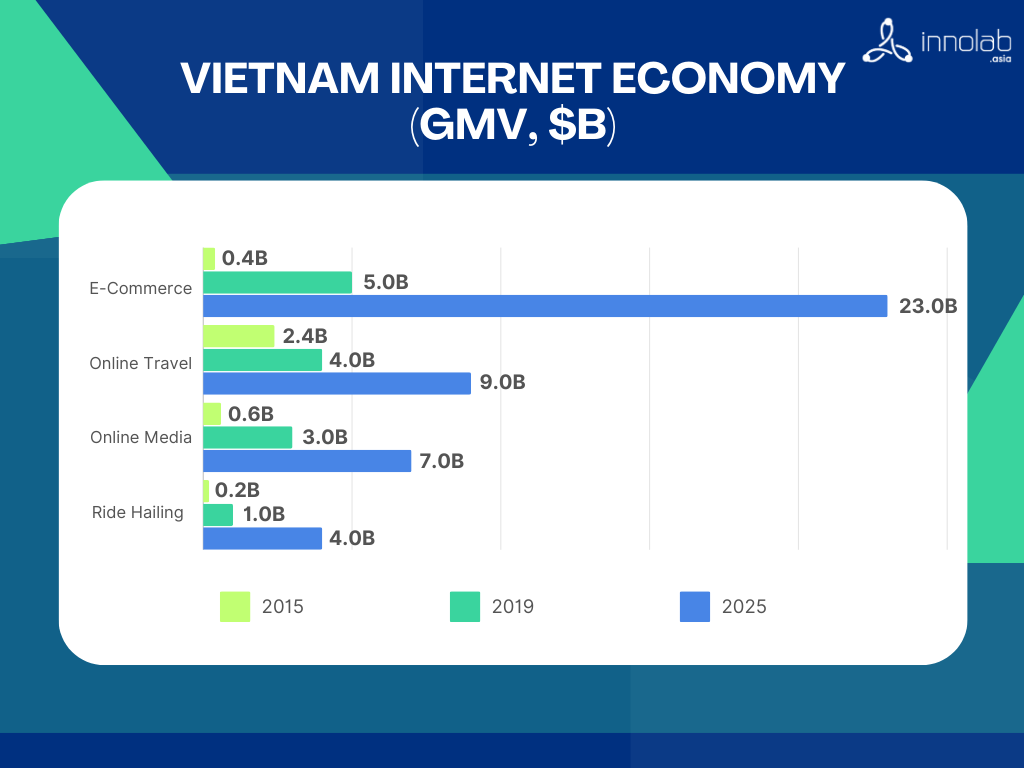
The plan also involves fully digitizing all energy sector-related documents, aiming to enhance both efficiency and modernization efforts. A core component of this initiative is the synchronized information system that integrates various energy industry sectors, facilitating smoother operations and better access to crucial data.
Vietnam is further advancing its energy infrastructure by expanding electricity access, to rank among the top three ASEAN countries by 2025. As part of this strategy, Vietnam Electricity (EVN) is accelerating the installation of e-meters, targeting a 95% installation rate by 2025 and full implementation by 2030. This will allow consumers to easily monitor their energy use while promoting transparency and efficiency in consumption.
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Growth and Trends
Vietnam saw a significant increase in FDI with over $4.29 billion recorded in early 2024, a 38.6% increase compared to the same period in 2023. This is fueled by global companies expanding or relocating their manufacturing to Vietnam, particularly in high-tech industries such as electronics and automotive (Vietnam Briefing, Vietnam’s Investment Surge in 2024) .
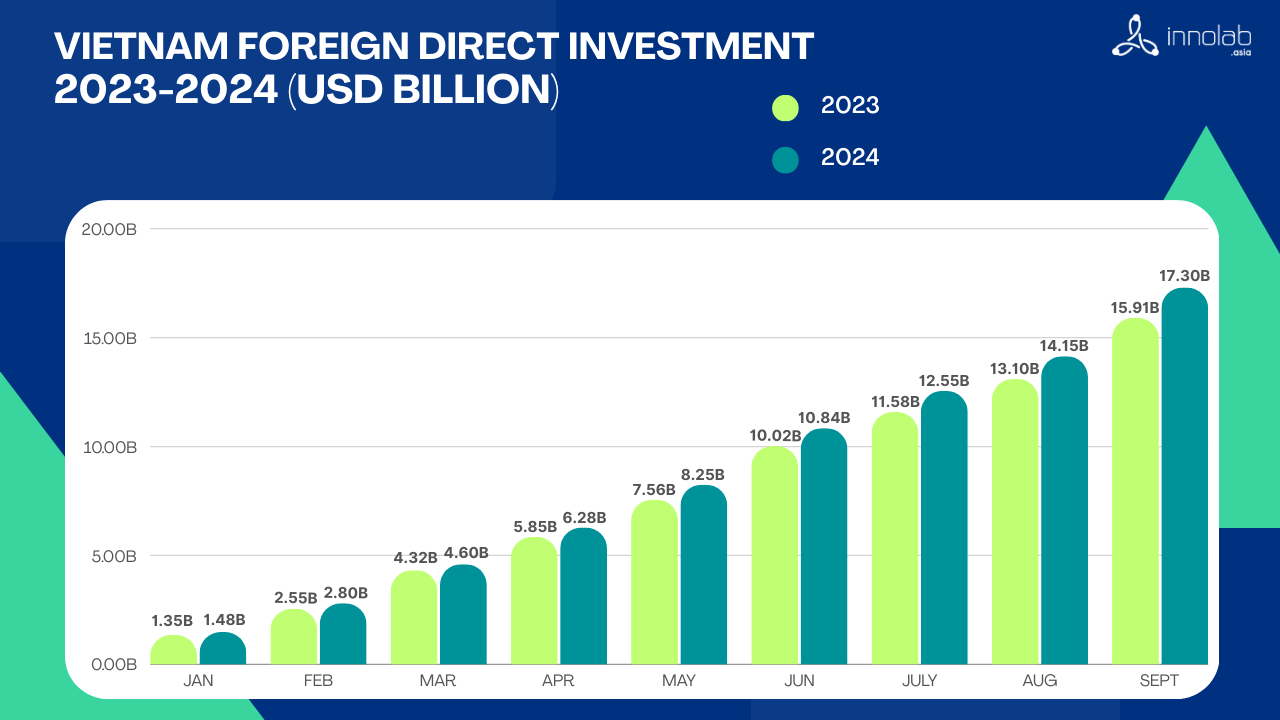
FDI in 2024 has been outperforming and producing more than 2023’s FDI. Vietnam is committed to boosting FDI by targeting high-value industries and diversifying its investment sources. Plans include tailored incentives for high-tech and green energy projects, such as tax breaks, land lease exemptions, and streamlined licensing processes. The government aims to attract global corporations seeking to relocate or expand their manufacturing bases due to geopolitical shifts, like the ongoing diversification of supply chains away from China. Vietnam also focuses on enhancing its position in the global supply chain through policies that encourage local production of components and value-added manufacturing
Additionally, it plans to liberalize its economy further by negotiating new trade agreements and expanding free trade zones to offer more favorable conditions for foreign investors. Investments will be directed towards infrastructure improvements, such as logistics networks and industrial park expansions, to accommodate the anticipated influx of FDI. The government also intends to bolster the legal framework for investment protection and intellectual property rights, making Vietnam a more attractive and secure environment for international businesses. (Vietnam Briefing, Vietnam’s 2024 Landscape Poised to See Robust Growth) .
Green Economy and Sustainability
Vietnam’s green economy is a key pillar in its long-term economic strategy, aiming to transform the nation into a leader in sustainability by 2050. The government has set ambitious goals to increase the green economy’s contribution to GDP, targeting $300 billion by mid-century from just $6.7 billion in 2020. The plan involves a substantial shift towards renewable energy, aiming for renewables to make up 67-71% of the energy mix by 2050, focusing on solar, wind, and clean hydrogen production. This transformation not only addresses climate change but also aligns with Vietnam’s goal of creating a competitive and resilient economy, positioning itself as a regional hub for green technology.
In addition to energy transition, Vietnam is also promoting sustainable industrial practices, green finance, and eco-friendly investments to accelerate the shift towards a low-carbon economy. For example, the country is implementing policies to encourage direct power purchases from renewable sources, making it easier for companies to meet sustainability targets. The government’s commitment to green growth includes fostering clean manufacturing processes and investing in sustainable infrastructure, which is expected to drive economic growth while reducing environmental impact. These initiatives underscore Vietnam’s broader strategy to integrate economic prosperity with environmental stewardship, thus attracting international investors who prioritize sustainability (Government News, National Green Growth Strategy for 2021-2030, vision towards 2050)
Potential Capability of Vietnam
Skilled Workforce and Outsourcing Potential
Vietnam’s workforce is recognized for its competitive skills and cost-effectiveness. The country has been ranked among the top destinations for IT outsourcing in Southeast Asia, thanks to its strong technical skills and relatively low labor costs compared to neighboring countries. This positions Vietnam as a strategic location for global companies seeking software development and IT services outsourcing.
Growth in the Digital Economy and Emerging Technologies
The country’s digital economy is expanding rapidly, growing 19% in 2023 to $30 billion, with expectations to continue outpacing GDP growth. This rapid expansion is expected to continue, consistently outpacing the country’s GDP growth. Ley advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, fintech, and 5G technologies are driving this progress. The widespread digital transformation across various industries in Vietnam presents substantial opportunities for foreign companies to collaborate and invest in the nation’s high-tech sectors (Saigon Times, Vietnam leverages Digital Transformation)
Government Support and Investment Incentives:
Vietnam’s government has introduced policies to attract foreign direct investment in high-tech industries, including tax incentives and regulatory support. These measures include preferential corporate income tax rates, tax holidays, and exemptions for businesses operating in prioritized sectors such as high-tech industries and environmental protection (Vietnam Briefing, Tax Incentives for Foreign Enterprises in Vietnam). Additionally, the government has approved the Digital Infrastructure Strategy by 2025, with a vision to 2030, highlighting its commitment to advancing the nation’s digital infrastructure. This proactive approach, combined with significant investments in digital infrastructure, signals Vietnam’s dedication to creating a favorable environment for global IT firms (Vietnam Briefing, Vietnam’s Digital Infrastructure Strategy)
Resilience in Venture Capital and Startup Ecosystem
Despite global economic downturns, Vietnam’s venture capital market has shown resilience. In 2023, the country secured $529 million in Venture Capital funding, focusing on sectors such as fintech, e-commerce, and AI. The presence of prominent global investors in Vietnam’s tech startups further boosts the perception of its growth potential (Vietnam Investment Review, Vietnam’s Startup Ecosystem in 2023) The support from summits such as the annual Vietnam Innovation Summit hosted by Innolab Asia, helps to provide help for tech and startup companies.

Pros and Cons of Investment in Vietnam
Pros
Rapid Economic Growth
Vietnam has been recognized as one of the fastest-growing countries in Asia, even worldwide. In 2023, Vietnam’s GDP grew by 5.05%, while witnessing a 5.66% year-over-year rise in Q1 of 2024. Despite the pandemic and leaving a vast amount of damage to countries, Vietnam was one of only a few countries able to maintain economic growth through 2020 and quickly get back on track in the latter half of 2023 after facing the gloomy economic landscape.
Demographic Advantage as a Growth Driver
Vietnam’s young and highly educated population of 96 million, with over 62% aged 15 to 59, forms a robust consumer base and workforce primarily consisting of Gen X and Millennials. By 2025, Gen Z is expected to comprise one-third of the working-age population, signaling increased purchasing power and productivity. This demographic strength, coupled with the country’s steady economic growth, positions Vietnam as a highly attractive investment destination across diverse sectors.
Competitive Labor Costs:
Vietnam’s labor costs are among the lowest in Asia while maintaining a high skill level, making it a favorite destination for outsourcing and manufacturing. This advantage enables businesses to improve profitability by reducing operational expenses without compromising quality. Sectors like textiles, electronics, and IT outsourcing are already thriving due to this cost-benefit. These labor costs are significantly lower than neighboring countries like Thailand and Malaysia.
Government Support and Trade Agreements:
Vietnam’s government actively supports foreign investment through policies like reduced corporate taxes, land incentives, and simplified regulations in special economic zones. Trade agreements, such as the EU-Vietnam Free Trade Agreement (EVFTA), reduce tariffs and increase market access for Vietnamese exports, encouraging multinational companies to establish operations.
Cons
Tax and Regulatory Challenges:
Vietnam’s tax systems, encompassing Corporate Income Tax and Value-Added Tax (VAT), is intricate and demands meticulous planning. Compliance often necessitates third-party consultation. The regulatory environment is complex, with extensive documentation and approvals that vary by region, making business setup particularly time-consuming for sectors like finance, healthcare, and technology
Infrastructure Bottlenecks:
Despite improvements, Vietnam’s infrastructure, especially transport and energy distribution, can impede business operations. Manufacturing regions face high energy demands, highlighting the need for further investment to ensure a reliable energy supply.
Language and Culture Barrier:
The Vietnamese language and cultural practices can lead to misunderstandings without local expertise or bilingual staff. Individuals may outwardly agree during discussions to avoid discomfort, even if they don’t fully understand or concur, necessitating a sensitive approach to foster effective communication and collaboration.
Economic and Policy Adjustments:
Vietnam’s adoption of the global minimum tax could affect its competitiveness for multinational enterprises. However, the government is developing alternative incentives to maintain the country’s investment appeal.
Digital Transformation in Vietnam
Vietnam has made substantial strides in digital transformation, positioning itself as one of the fastest-growing digital economies in Southeast Asia, with a projected market value of around $45 billion by 2025. Key advancements are particularly notable in e-commerce, digital payments, and online services like tourism, where sectors have seen rapid expansion fueled by a young, tech-savvy population and government-led digitalization programs. The Vietnamese government has prioritized four core pillars in digital transformation: ICT industry growth, economic digitalization, digital governance, and robust digital infrastructure (VnEconomy, Vietnam Prioritizes Digital Transformation with Ambitious 2024 Goals).
Digital Economy :
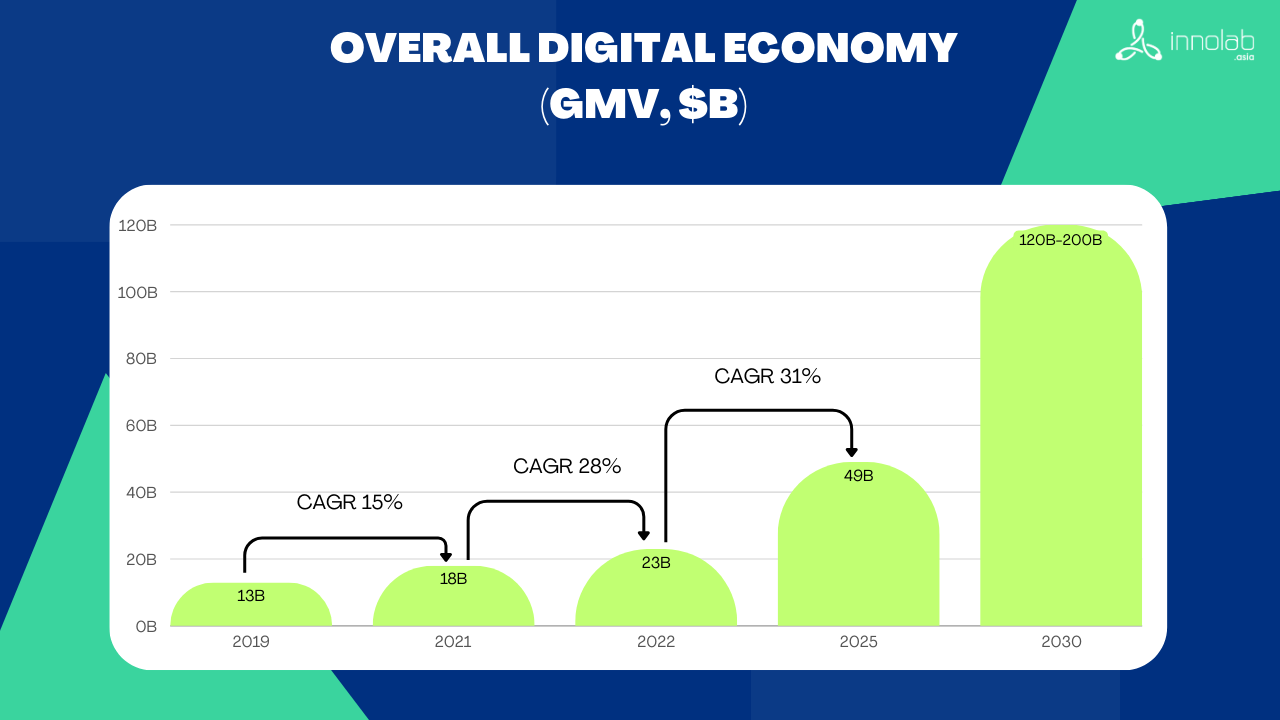
Vietnam aims for its digital economy to contribute 30% of GDP by 2030. To achieve this, the government is focusing on sectors like e-commerce, digital payments, fintech, and emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT). Initiatives supporting startups and innovation include the National Technology Innovation Program, the National Innovation Center, and the National AI Strategy, which aspires to position Vietnam as a leading AI hub in Southeast Asia (Open Development Mekong, Vietnam Digital Transformation Agenda).
Digital Government
The Vietnamese Government has launched comprehensive plans to accelerate digital transformation. The 2024 Work Plan emphasizes enhancing the IT industry, digitizing economic sectors, improving digital governance, and managing digital data. These initiatives aim to elevate Vietnam to the ranks of digitally advanced nations.(VnEconomy, Vietnam Prioritizes Digital Transformation with Ambitious 2024 Goals).
Digital Society:
Vietnam strives to make digital transformation inclusive, ensuring everyone can access technology and services. Digital literacy programs, in partnership with schools and private groups, focus on equipping rural and underserved communities with essential skills.
Efforts to provide affordable internet, including subsidies for remote areas, help expand connectivity. The government also promotes user-friendly platforms to ensure accessibility for people with disabilities.
The Digital Transformation Center leads these initiatives, driving innovation and fostering an inclusive digital future for all (Saigon Technology, Driving Innovation: Digital Transformation in Vietnam)
Most Prospective Industry 4.0 in Vietnam
Vietnam is rapidly advancing in the 4th industrial revolution, leveraging emerging technologies to boost economic growth and competitiveness. Most prospective industries include Manufacturing and High-Tech Production, Agriculture and Food Processing, and Logistics and Supply Chain Management. These sectors are adopting industry 4.0 innovations to enhance efficiency and productivity. The government’s proactive approach, including partnerships with global tech leaders, aims to make Vietnam a regional hub for digital transformation and sustainable development, positioning it strongly on the global stage.
Manufacturing and High-Tech Production:
Vietnam’s manufacturing sector is the backbone of its economy, contributing over 20% to GDP. Industry 4.0 technologies like automation, robotics, and IoT are revolutionizing factories, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. Electronics manufacturing, in particular, has experienced significant growth, with global giants like Samsung, Intel, and Foxconn investing heavily in Vietnam as a hub for high-tech production.
Smart manufacturing is also gaining traction, with companies leveraging data analytics to improve efficiency and reduce costs. The government is fostering this transformation by creating industrial zones and offering incentives for adopting Industry 4.0 technologies. As global supply chains shift, Vietnam is well-positioned to capitalize on its manufacturing capabilities.
Agriculture and Food Processing:
Vietnam is integrating smart farming practices and precision agriculture to enhance productivity and sustainability. Technologies like drones, sensors, and AI are being utilized to improve crop yields and resource management, aligning with global trends towards sustainable agriculture.
Agriculture 4.0 leverages Industry 4.0 technologies across agricultural supply chains to boost efficiency and improve community well-being. Agriculture 4.0 involves the application of inter-connected technology to create new production and supply chain management options, such as sensors and the IoT to improve on-farm management, robotics to reduce labor intensity in production and logistics operations, AI, and big data to inform production decisions and optimize yield, and Distributed Ledge Technology to track provenance.
Logistics and Supply Chain Management:
As global manufacturing hub, Vietnam is investing in modernizing its logistics sector. The adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, including data analytics and automated warehousing, is optimizing supply chains, and enhancing efficiency in trade and distribution networks.
Logistics 4.0 encompasses the integration of ICT and Industry 4.0 technologies by logistic companies to enable coordinated, efficient, and sustainable management of operations both within the company and across supply chains. This transformation includes transitioning from analog to digital platforms and implementing advanced Industry 4.0 technologies throughout the supply chain, covering areas such as procurement, warehousing, inventory management, transportation, and reverse logistics.
Education and Training:
The shift to “Education 4.0” is transforming Vietnam’s education system, with universities and schools adopting technologies like virtual reality, online learning platforms, and AI-driven personalization. This transition is crucial to developing a skilled workforce capable of thriving in a technology-driven economy.
Edtech startups are playing a significant role in bridging gaps, offering affordable and innovative solutions for both urban and rural areas. Government initiatives and partnerships with international organizations are accelerating this transformation, ensuring Vietnam’s education system aligns with global Industry 4.0 standards.
In Conclusion
Vietnam’s Investment Landscape in 2024 is marked by strategic emphasis on infrastructure expansion, digital transformation, and green growth. These initiatives, spearheaded by government support and favorable policies, are designed to position Vietnam as a competitive, modern economy with Southeast Asia. Significant investment in high-tech manufacturing, renewable energy, and digital services aims to attract global companies and boost Foreign Direct Investment (FDI). The country is enhancing its infrastructure, with projects like expressway expansions, metro line upgrades, and the integration of smart city technologies, laying a foundation for sustainable and efficient growth .
Digital transformation is central to Vietnam’s development, driving growth in sectors such as e-commerce, fintech, and smart cities. Government-backed initiatives aim to digitize public services and administrative processes, with AI and IoT enabling efficiency across industries, Industry 4.0 technologies are transforming manufacturing through automation and smart factories, improving productivity and product quality. Agriculture is also evolving, with precision farming technologies enhancing sustainability, while logistics and supply chain management are modernizing with data-driven approaches, optimizing Vietnam’s position in global trade networks.
Despite these promising advancements, challenges such as regulatory complexity, infrastructure gaps, and cultural nuances remain. Business setup can require navigating extensive documentation, and some infrastructure, particularly in energy and transportation, needs further development to fully support economic growth. However, Vietnam’s proactive improvements in digital infrastructure, skilled workforce, and commitment to green initiatives make it an increasingly attractive destination for international investors. By aligning with global trends in sustainability and technology, Vietnam is set to solidify its role as a key economic player in Asia, offering substantial opportunities for long-term investment.
References
e-Conomy SEA by Google, Temasek, Bain: Southeast Asia’s digital economy research programme. (2023). [online] e-Conomy SEA report. Available at: https://services.google.com/fh/files/misc/e_conomy_sea_2023_report.pdf.
Dharmaraj, S. (2026). Catalysing Green Growth: Vietnam’s Ambitious Digital Transformation Agenda. In OPENGOV. OPENGOV. https://opengovasia.com/2024/04/17/catalysing-green-growth-vietnams-ambitious-digital-transformation-agenda/
Vietnam 2024 Outlook | The Investor’s Guide to growth. (n.d.-b). KPMG. https://kpmg.com/vn/en/home/insights/2024/03/vietnam-2024-outlook-the-investor-guide-to-growth.html
Pham, A. (2024, October 23). Vietnam investment snapshot (2024) | Acclime Vietnam. Acclime Vietnam. https://vietnam.acclime.com/guides/vietnam-investment-snapshot-2024/
Vietstock. (2020b, January 17). Vietnam targets to have 100,000 digital firms by 2030 | Vietstock. Vietstock. https://en.vietstock.vn/2020/01/vietnam-targets-to-have-100000-digital-firms-by-2030-38-376385.htm
Briefing, V. (2024f, August 28). Vietnam’s investment surge in 2024: key trends and opportunities. Vietnam Briefing News. https://www.vietnam-briefing.com/news/vietnams-investment-surge-in-2024-key-trends-and-opportunities.html/
Briefing, V. (2024c, April 2). Vietnam’s 2024 FDI Landscape: Opportunities and emerging trends. Vietnam Briefing News. https://www.vietnam-briefing.com/news/vietnams-2024-fdi-landscape-opportunities-incentives-and-emerging-trends.html/
En.Baochinhphu.Vn. (2021b, November 7). National Green Growth Strategy for 2021-2030, vision towards 2050. https://en.baochinhphu.vn/national-green-growth-strategy-for-2021-2030-vision-towards-2050-11142515.htm
TRADING ECONOMICS. (n.d.-b). Vietnam GDP Annual growth Rate. https://tradingeconomics.com/vietnam/gdp-growth-annual#:~:text=GDP%20Annual%20Growth%20Rate%20in,the%20third%20quarter%20of%202021.
Away Digital Teams. (2023, November 23). Vietnam’s IT outsourcing dominance. https://awaydigitalteams.com/blog/vietnams-it-outsourcing-dominance/?utm_source=chatgpt.com
An, D. (2024, October 27). Vietnam leverages digital transformation for economic growth – report – The Saigon Times. The Saigon Times. https://english.thesaigontimes.vn/vietnam-leverages-digital-transformation-for-economic-growth-report/?utm_source=chatgpt.com
Tax incentives for foreign enterprises in Vietnam – Vietnam Guide | Doing Business in Vietnam. https://www.vietnam-briefing.com/doing-business-guide/vietnam/taxation-and-accounting/tax-incentives-for-businesses
Briefing, V. (2024h, October 17). Vietnam’s digital infrastructure strategy opens investment opportunities. Vietnam Briefing News. https://www.vietnam-briefing.com/news/vietnams-digital-infrastructure-strategy-2025-new-opportunities-for-foreign-investors.html/#:~:text=Overview%20of%20Vietnam’s%20Digital%20Infrastructure,percent%20population%20coverage%20by%202030.
Vietnam Investment Review. (2024a, April 29). $529 million funneled into Vietnam’s startup ecosystem in 2023. Vietnam Investment Review – VIR. https://vir.com.vn/529-million-funneled-into-vietnams-startup-ecosystem-in-2023-110728.html?
Vietnam Prioritizes Digital Transformation with Ambitious 2024 Goals. (2024b, April 21). Vietnam Economic Times | VnEconomy. https://en.vneconomy.vn/vietnam-prioritizes-digital-transformation-with-ambitious-2024-goals.htm
Nnguyen. (2023, December 19). Vietnam Digital Transformation Agenda – Open Development Vietnam. Open Development Vietnam – Sharing Information About Vietnam and Its Development With the World. https://vietnam.opendevelopmentmekong.net/topics/vietnam-digital-transformation-agenda/
Pham, T. (2024, November 20). Driving Innovation: Digital transformation in Vietnam. Saigon Technology. https://saigontechnology.com/blog/digital-transformation-in-vietnam/



