Introduction
As one of Southeast Asia’s fastest-growing economies, Vietnam has attracted the attention of international investors in recent years. With a young population, growing middle class, and strategic geographic location, the country offers numerous investment opportunities. However, potential investors should also consider the challenges and risks associated with this emerging market. In this comprehensive analysis, we will explore the pros and cons of investing in Vietnam in 2023, providing crucial information for informed investment decisions.
Pros of Investing in Vietnam
-
Strong Economic Growth
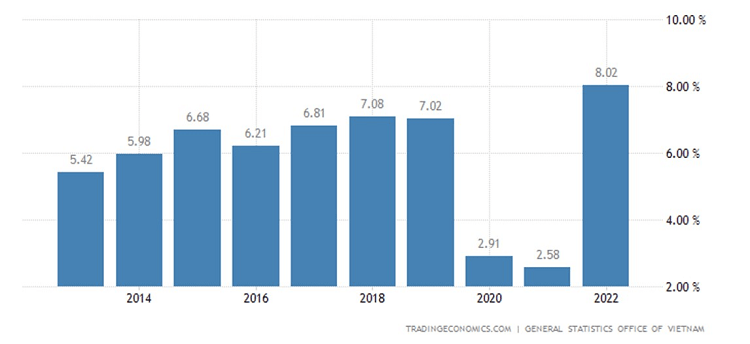
According to TRADING ECONOMICS, Vietnam’s GDP growth rate in 2022 was 8.02%, making it one of the fastest-growing economies in the region. This growth is fueled by a shift towards manufacturing, an expanding middle class, and increasing foreign direct investment (FDI). The Vietnamese government’s pro-business policies, including tax incentives and the establishment of special economic zones, have also contributed to this growth.
-
Young and Skilled Workforce
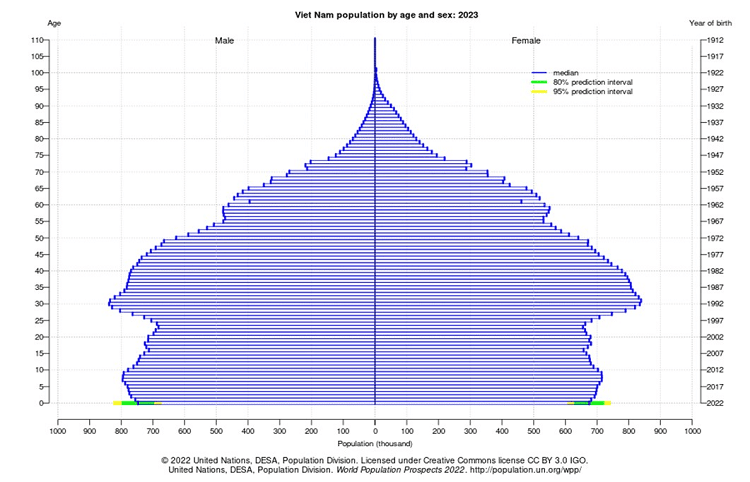
With a median age of approximately 32.8 years in 2023, Vietnam has a young and dynamic workforce that offers a competitive advantage for investors. The literacy rate is over 95%, and the government has made significant investments in education, particularly in STEM fields. This has resulted in a skilled labor force that is well-equipped to meet the demands of modern industries.
-
Strategic Geographic Location
Vietnam’s strategic location, with a coastline along the South China Sea, makes it an ideal hub for trade and manufacturing. The country shares borders with China, Laos, and Cambodia, facilitating regional trade and integration. Vietnam is also a member of various regional trade agreements, such as the ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA) and the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP), which further enhances its trade prospects.
-
Growing Middle Class
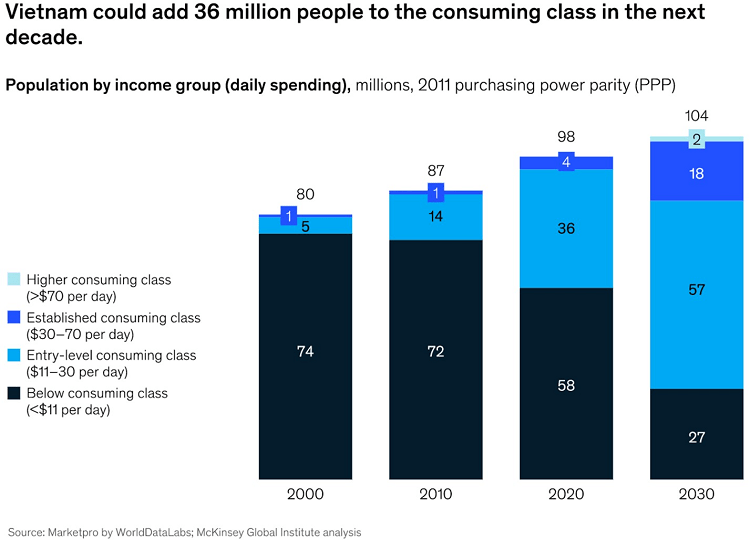
According to new research published by World Data Lab (UK), Vietnam’s middle class will increase by 23,2 million people by 2030. According to the standards of this organization, the middle class consists of households with per capita expenditures between 11 and 110 USD per day. According to a report published by Statista in March 2021, the annual growth rate of the middle class in Vietnam between 2016 and 2021 is 10.1%, the greatest rate in Southeast Asia.
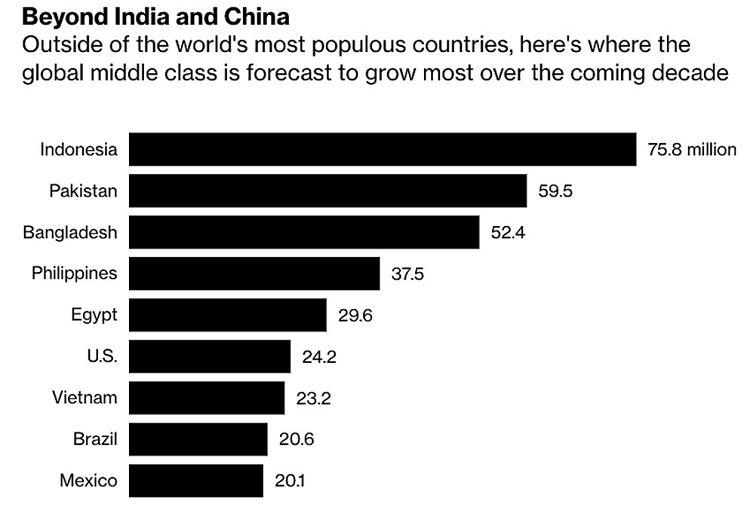
Source: Bloomberg
This expanding middle class has greater purchasing power and a rising demand for high-quality products and services, offering vast opportunities for businesses in sectors such as retail, healthcare, and real estate.
-
Increasing Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
Vietnam has become an attractive destination for FDI, Data from the Ministry of Planning show the country saw more than $27.72 billion in foreign direct investments pumped into different sectors across provinces in 2022. The government has actively pursued policies to attract foreign investment, including tax incentives, streamlined regulations, and the establishment of special economic zones. Key industries attracting FDI include manufacturing, real estate, and energy.
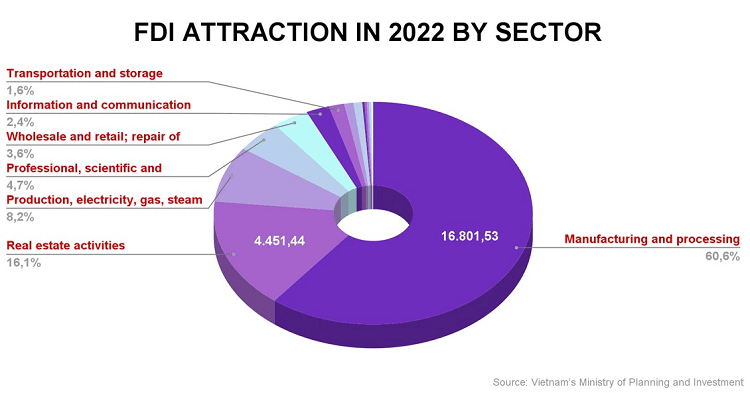
Cons of Investing in Vietnam
-
Infrastructure Challenges
Despite the government’s efforts to improve Vietnam’s infrastructure, challenges remain, particularly in transportation and energy. Traffic congestion, limited public transportation, and underdeveloped seaports can hinder logistics and trade. Furthermore, the country’s growing energy demand is straining the existing power grid, resulting in occasional power outages.
-
Bureaucracy and Corruption
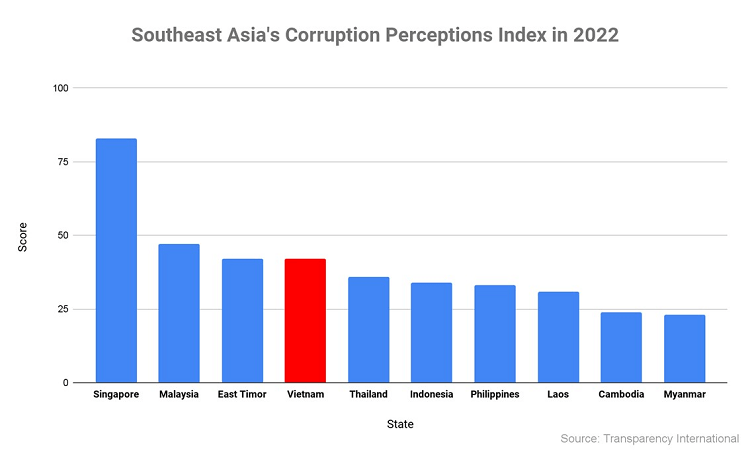
While the Vietnamese government has made progress in streamlining regulations, investors still face bureaucratic hurdles and a complex legal system. Corruption remains a significant concern, with Vietnam ranking 77th out of 180 countries in Transparency International’s 2022 Corruption Perceptions Index. Navigating the business environment can be time-consuming and costly, particularly for foreign investors unfamiliar with local regulations and practices.
-
Intellectual Property Protection
Inadequate intellectual property (IP) protection can be a barrier for investors, particularly in industries that rely heavily on patents and trademarks. Although Vietnam has made strides in strengthening its IP laws, enforcement remains weak, and instances of counterfeiting and piracy persist.
-
Currency and Exchange Rate Risks
The Vietnamese dong (VND) has a history of instability, and while the government has worked to maintain exchange rate stability, investors should be aware of the potential risks associated with currency fluctuations. Additionally, restrictions on foreign exchange transactions and repatriation of profits may pose challenges for international investors.
-
Competition and Market Saturation
With a rapidly growing economy and increasing FDI, competition in certain industries can be fierce. Some sectors, such as retail and real estate, have seen market saturation, making it difficult for new entrants to succeed without a strong competitive advantage or niche market focus.
Investment Opportunities and Strategies
Despite the challenges, Vietnam offers numerous investment opportunities for informed investors. To capitalize on these opportunities, consider the following strategies:
-
Target High-Growth Sectors
Focus on industries with strong growth potential, such as manufacturing, renewable energy, and technology. Vietnam’s government has identified these sectors as priorities for development, and they are likely to benefit from supportive policies and increasing FDI.
-
Leverage the Growing Consumer Market
As Vietnam’s middle class expands, so too does demand for high-quality products and services. Investors can capitalize on this trend by targeting sectors such as healthcare, education, retail, and real estate.
-
Partner with Local Businesses
To navigate Vietnam’s complex business environment, consider partnering with local businesses that have a deep understanding of the market, regulations, and cultural norms. Joint ventures and strategic partnerships can provide valuable local insights and access to resources, helping to mitigate risks and enhance success.
-
Conduct Thorough Due Diligence
Before investing in Vietnam, conduct comprehensive due diligence to fully understand the market, competition, regulations, and potential risks. This may include consulting with local experts, conducting market research, and seeking legal advice.
-
Stay Informed and Adapt
The Vietnamese market is constantly evolving, and investors must stay informed about the latest trends, regulations, and opportunities. Continually reassess your investment strategy, and be prepared to adapt to changes in the market and regulatory environment.
Conclusion
Vietnam’s market presents both significant opportunities and challenges for investors. By understanding the pros and cons of investing in this emerging economy, conducting thorough due diligence, and implementing strategic investment approaches, investors can capitalize on the growth potential of Vietnam’s market in 2023 and beyond.
If you need any further consultancy, please kindly email us at hello@innolab.asia.
References:
TRADING ECONOMICS. (2023). Vietnam Full Year Gdp Growth – 2022 Data – 2023 Forecast – 2010-2021 Historical (tradingeconomics.com). Retrieved from https://tradingeconomics.com/vietnam/full-year-gdp-growth
database.earth. (2023). Median Population Age of Viet Nam 1950-2023 & Future Projections Retrieved from https://database.earth/population/viet-nam/median-age
Asian Development Bank. (Feb 2020). Viet Nam Secondary Education Sector Assessment, Strategy, and Road Map. Retrieved from https://www.adb.org/sites/default/files/institutional-document/561121/viet-nam-secondary-education-assessment.pdf
The World Bank. (Oct 2020). Improving The Performance Of Higher Education In Vietnam Strategic Priorities and Policy Options. Retrieved from https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/347431588175259657/pdf/Improving-the-Performance-of-Higher-Education-in-Vietnam-Strategic-Priorities-and-Policy-Options.pdf
Vietnam’s Ministry of Planning and Investment. (Dec 2022). December 2022 report on foreign direct investment (FDI). Retrieved from https://www.mpi.gov.vn/en/Pages/tinbai.aspx?idTin=56367&idcm=122
Bloomberg. (2021). More Than 1 Billion Asians Will Join Global Middle Class by 2030. Retrieved from https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2021-09-02/more-than-1-billion-asians-will-join-global-middle-class-by-2030
McKinsey Global Institute. (Dec 2021). The new faces of the Vietnamese consumer. Retrieved from https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/future-of-asia/the-new-faces-of-the-vietnamese-consumer
Transparency International. (2023). Corruption Perceptions Index 2022. Retrieved from https://www.transparency.org/en/cpi/2022
Vietnam Association of Realtors (Jan 2023). Vietnam Real Estate Market Report 2022. Retrieved from https://vars.com.vn/uploads/up/vars/marketnews/2023/01/13/04/05/var1673535949_2888.pdf



